


Unfortunately this service has become quite unreliable since public gateway servers seem to be unable to scale with the demand for prefixes.Ħrd is the provider internal equivalent of 6to4. All 6to4 prefixes are in the 2002::/16 network and are /48 bits long (16bits for 2002::/16 and 32bits from the IPv4 address of the gateway). Both use the 6in4 encapsulation to transport IPv6 packets inside IPv4 packets between the border gateway of the local network and the gateway servers outside.Ħto4 is a public service, everybody can configure a gateway to use it - no subscription is necessary, since gateways will always know where to route responses based on the prefix. With both mechanisms you can assign an IPv6 prefix to an entire network based on the IPv4 address of the gateway.
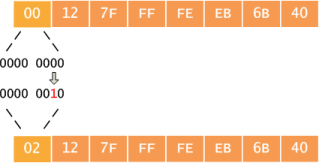
Please use hexadecimal notation with the relevant 32 bits to the far right.Ħto4 and 6rd are transitional mechanisms that will be used until native IPv6 is universally available. Depending on your application you may have to shift the IPv6 segments. This form allows you to convert from IPv4 to IPv6 and back. In some configurations IPv4 addresses can be written or used in IPv6 notation or they become part of an IPv6 address. Link Broadcast - this is sent to all hosts on the same network link, but does not cross routers there is no default gateway or broadcast for multicasting Multicasts (former Class D network) - Warning: the data shown when you click this network is not completely accurate - e.g. TEST-NET-2, Documentation and examples TEST-NET-3, Documentation and examples Network benchmark tests, this should never be used in production networks. MacOS and Linux with Avahi installed) and are only usable for local communication in the LAN segment. These are automatically generated by some operating systems and (e.g. The entire 127.*.*.* network is reserved for (host-)local networking. Is the localhost address, used by each host to talk to itself, there is always a special loopback interface preconfigured with this address, you never assign it to a real network device. The whole network 0.*.*.* is reserved for special purposes (like DHCP).ġ0.*.*.* 172.16.*.* - 172.31.*.* 192.168.*.*Īre private addresses - you can use them freely within your own LAN. The "ANY" address that is used by programs to speak to all network interfaces, it is never used directly. Normally people don’t change the MAC addresses of their interfaces which means that EUI-64 will change the 7 th bit from 0 to 1 most of the time.The following special addresses and networks exist in IPv4: When you change the MAC address this bit has to be set to 1. A “built in” MAC address will always have this bit set to 0. The 7 th bit represents the universal unique bit. This means that if it’s a 0 you need to make it a 1, and if it’s a 1 it has to become a 0. To do this you have to convert the first two hexadecimal characters of the first byte to binary, lookup the 7 th bit and invert it. It doesn’t include the final step which is “inverting the 7 th” bit. So if my MAC address would be then this is what the interface ID will become:Ībove you see how we split the MAC address and put FFFE in the middle. We invert the 7 th bit of the interface ID.
#IPV6 MAC ADDRESS CONVERTER 64 BIT#
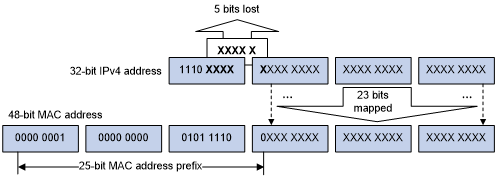
We insert “FFFE” in between the two pieces so that we have a 64 bit value.We take the MAC address and split it into two pieces.Here’s what we will do to fill the missing bits: What are we going to do with the missing bits? However, a MAC address is 48 bit and the interface ID is 64 bit. An IPv6 device will use the MAC address of its interface to generate a unique 64-bit interface ID. EUI-64 (Extended Unique Identifier) is a method we can use to automatically configure IPv6 host addresses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
